Understanding the Legality of Bear Traps in the United States: Laws, Requirements, and Safe Practices
Introduction: Bear Traps in America-A Legal Overview
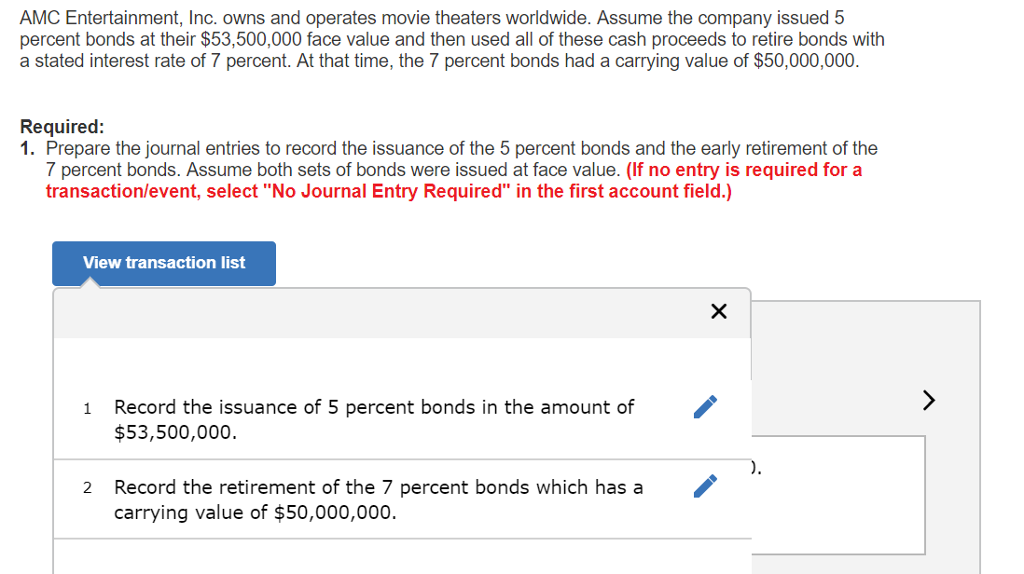
The use of bear traps is a subject governed by a web of federal, state, and local regulations in the United States. While trapping bears is permitted in certain jurisdictions, the legality, acceptable trap types, permit requirements, and animal welfare standards differ significantly across the country. Anyone considering the use of bear traps must understand the legal obligations, safety measures, and ethical considerations involved. This guide breaks down the essential facts, provides actionable steps for compliance, and discusses alternatives for nuisance bear management.
Where Are Bear Traps Legal?
Bear trapping is not universally permitted across the United States. In many states, specific forms of trapping are allowed but are subject to strict regulations. For example, Maine allows the taking of black bears by trapping, but only with cable restraints or large cage-type live traps. The state issues a limited number of permits and restricts the number of bears one may trap per season. In contrast, on federal lands such as those managed by the National Wildlife Refuge System, the use of body-gripping bear traps (including steel-jaw leghold traps, snares, and Conibear traps) is banned or heavily restricted due to animal welfare concerns and public safety risks [1] . Always consult your state’s wildlife agency or fish and game department for current trapping laws in your area. In some states, trapping bears is not permitted at all, or is allowed only for nuisance wildlife management under special authorization.

Source: fanpop.com
Permitted Trap Types and Legal Requirements
States that allow bear trapping typically restrict the types of traps that may be used. In Maine, only cable restraints (foothold cable traps) and cage-type live traps are lawful for capturing bears. Steel-jaw leghold and body-gripping traps are prohibited in most circumstances due to their potential to cause severe injury to animals and risks to non-target species [2] . For cage traps, construction standards are enforced to ensure animal safety: traps must be well-ventilated, free from sharp edges, and large enough to allow a bear to turn around. In Florida, cage traps are permitted under specific size and monitoring requirements, and a no-cost wildlife trapping permit is necessary [3] .
Trap tending and inspection intervals are also heavily regulated. For instance, most states require that traps be checked at least once every 24 hours. Electronic monitoring devices may be allowed in some jurisdictions, but physical inspections remain the gold standard for animal welfare. In New Hampshire, state law also mandates the construction of a guardrail and clear signage around any set bear trap to protect the public and wildlife [4] .

Source: seethewild.org
Permits, Registration, and Reporting
Obtaining a permit is mandatory in nearly every state where bear trapping is legal. Maine, for example, requires a distinct bear trapping permit, with separate fees for residents and nonresidents. The permit process typically involves providing personal information, proof of prior trapping experience or education, and sometimes passing a wildlife trapper safety course. After taking a bear, trappers must follow specific tagging, transportation, and registration protocols. These often include reporting the capture to state authorities within a set timeframe and bringing the animal for inspection and data collection.
For smaller-scale or nuisance trapping (such as landowners addressing problem bears), streamlined or no-cost permits may be available. However, these are generally limited to cage traps of specific dimensions and must comply with all other legal restrictions. In all cases, it is critical to review and follow the latest guidance from your state wildlife agency before setting any bear trap.
Animal Welfare and Public Safety
The use of bear traps raises important animal welfare and public safety concerns. Laws are designed to minimize suffering and protect non-target species, pets, and humans. For example, federal directives prohibit the use of steel-jaw traps with teeth or spiked jaws, and require the use of pan-tension devices to reduce accidental captures [5] . Many states also require signs and barriers to warn the public and prevent accidental injury near active trap sites.
In addition to legal requirements, ethical best practices suggest using cage-type live traps wherever possible, releasing non-target animals promptly, and seeking alternatives to lethal control. Professional wildlife removal operators often employ non-lethal deterrents and exclusion techniques before resorting to trapping. If you encounter a nuisance bear, contact your state’s wildlife agency for guidance on safe and legal response options.
Step-by-Step Guidance for Lawful Bear Trapping
If you are considering trapping a bear, follow these steps to ensure compliance and safety:
- Research Local Laws: Start by visiting your state’s official wildlife agency website or contacting their office directly. Search for terms like “bear trapping regulations” and “wildlife trapping permits.” Laws can change frequently, so use only current sources.
- Obtain Permits: Apply for the appropriate trapping permit. This may require an application form, fee payment, and sometimes proof of training or experience. For example, in Maine, both residents and nonresidents must secure a bear trapping permit before setting traps [2] .
- Choose Legal Trap Types: Use only legal traps, such as cable restraints or certified cage traps. Ensure that your equipment meets all state-mandated specifications for size, ventilation, and safety.
- Site Selection and Setup: Set traps away from public areas, and never within restricted zones such as near solid waste disposal sites without permission. Erect mandated signage and barriers where required by law.
- Tend and Inspect Traps: Check traps at least once every 24 hours, and release or dispatch animals humanely and in accordance with state protocols. Keep accurate records of all activity.
- Register and Report: Follow your state’s requirements for tagging, transporting, and registering any bear taken. In most cases, this involves submitting a report and presenting the animal for inspection.
- Consider Alternatives: If you are dealing with nuisance bears, explore non-lethal deterrents and exclusion methods first. Many states provide resources or referrals to professional wildlife removal services.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Bear trapping is complex and fraught with potential legal pitfalls. Some common challenges include:
- Changing Laws: Trapping regulations can change with little notice. Always verify the latest requirements before acting.
- Non-Target Captures: Even with best practices, non-target species may be caught. Use approved traps and check them frequently to minimize harm.
- Permit Delays: Start the permitting process early and keep copies of all documentation.
- Public Opposition: Be prepared for scrutiny from neighbors or animal welfare groups. Adhere strictly to legal and ethical standards, and keep communication open with authorities.
Alternatives to Bear Trapping
Due to the risks and responsibilities involved, many wildlife agencies and advocacy groups recommend non-lethal alternatives for dealing with bears. These include improved waste management, electric fencing, noise deterrents, and chemical repellents. Some agencies offer technical assistance or can remove nuisance bears under special circumstances. If you need help, contact your state’s Department of Fish and Wildlife or similar agency and request advice on humane bear conflict resolution.
Summary: Stay Informed and Compliant
The legality of bear traps in the U.S. is highly dependent on your location, the type of trap, and the intended use. Always consult official resources, secure necessary permits, and consider non-lethal alternatives to ensure compliance with both the letter and spirit of the law. For the latest regulations, search for your state’s wildlife agency by name and review their official trapping guidelines. If in doubt, contact the agency directly before taking any action.
References
- [1] Animal Welfare Institute (2023). Refuge from Cruel Trapping Act overview and legislative update.
- [2] Maine Department of Inland Fisheries & Wildlife (2024). Bear Trapping: Laws & Rules.
- [3] Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (2024). Trap Types: Current Status and Possible Changes.
- [4] New Hampshire Revised Statutes (2024). Protection of Bear Traps.
- [5] USDA APHIS Wildlife Services (2021). Wildlife Services Directive 2.450: Use of Traps.
MORE FROM couponnic.com