How Autonomous Vehicles Are Transforming the Future of Agriculture

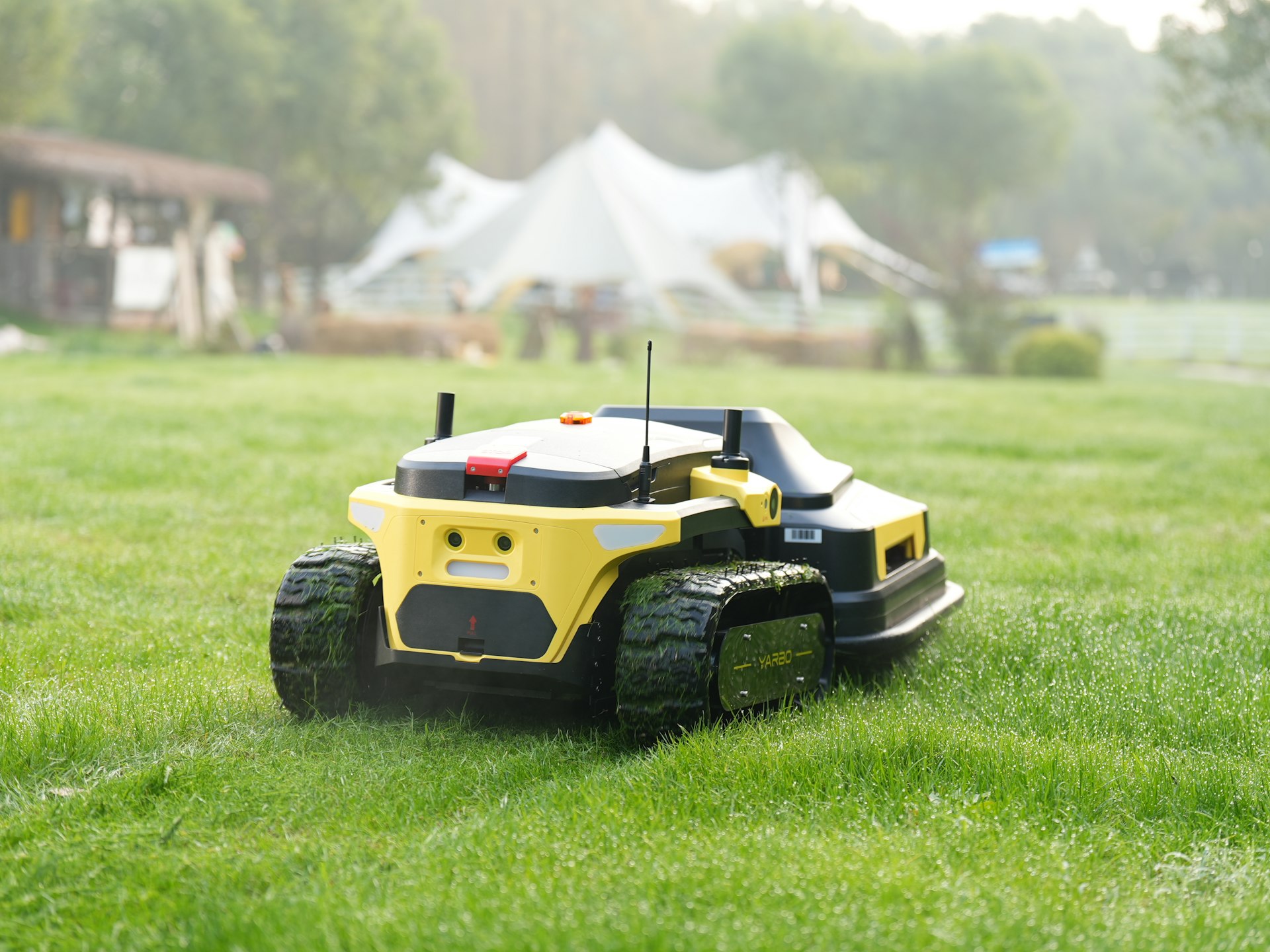
Photo by Yarbo Global on Unsplash
The Rise of Autonomous Agricultural Vehicles: A New Era in Farming
The agricultural sector is undergoing a radical transformation. As global demand for food increases and labor shortages persist, the need for higher productivity, efficiency, and sustainability has never been more pressing. Autonomous agricultural vehicles-such as driverless tractors, robotic harvesters, and smart drones-are emerging as the cornerstone of modern, technology-driven farming. By 2025, the autonomous agricultural machinery market is projected to surpass $15 billion globally, with over 60% of new machinery featuring autonomous or semi-autonomous capabilities [1] [2] .
Core Technologies Powering the Revolution
At the heart of autonomous agricultural vehicles are several converging technologies:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: These digital brains analyze massive datasets to optimize navigation, crop management, and predictive maintenance. AI enables machines to adapt to changing field conditions, while machine learning allows continuous self-improvement for tasks like targeted spraying or weed removal [1] [4] .
- Advanced Sensing, GPS, and Computer Vision: GPS-guided navigation ensures precise fieldwork. Onboard sensors (including LIDAR, radar, and hyperspectral cameras) scan crop health, field conditions, and obstacles. Computer vision distinguishes crops from weeds and supports delicate operations, such as fruit picking or targeted irrigation [1] .
- Internet of Things (IoT) & Remote Connectivity: IoT-enabled platforms provide real-time monitoring, diagnostics, and fleet coordination. Cloud integration means farm managers can remotely control machinery and access data from anywhere [1] .
- Robotics and Automation: Modern robots perform seeding, weeding, and harvesting with higher precision than ever. Drones deliver crop monitoring and aerial spraying, expanding access to challenging terrain [1] .
These breakthroughs are not theoretical-they are being deployed on farms worldwide, reshaping everyday operations and long-term planning.
Practical Benefits: Efficiency, Productivity, and Sustainability
Autonomous agricultural vehicles deliver a range of practical benefits:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity Autonomous tractors and harvesters can operate 24/7, maintaining consistent precision and output. Multiple units can work together, scaling operations and minimizing downtime. This reduces labor dependency, optimizes input use (such as seeds and fertilizers), and helps farmers manage larger areas with fewer resources [3] .
2. Improved Safety and Strategic Human Resource Use By automating repetitive and hazardous tasks, autonomous vehicles reduce workplace injuries and free up skilled workers for higher-value activities. For example, removing humans from pesticide application or heavy machinery operation lowers risk and liability [3] .
3. Sustainability and Resource Optimization These vehicles support precision agriculture practices, using data analytics to apply water, fertilizer, and pesticides only where needed. This reduces environmental impact, minimizes soil degradation, and maximizes crop yields [2] .
Adoption Roadmap: How to Access and Implement Autonomous Technologies
If you are interested in adopting autonomous agricultural vehicles or integrating smart technologies on your farm, consider these actionable steps:
- Assess Your Needs and Resources: Evaluate your current operations and identify areas where automation could deliver the greatest value (e.g., planting, harvesting, spraying).
- Research Available Solutions: Leading manufacturers and technology firms-including John Deere, CNH Industrial, and AGCO-offer autonomous tractors, robotic sprayers, and fleet management platforms. Visit the official websites of these companies or reputable agricultural technology expos to explore product specifications and case studies.
- Explore Financing and Service Models: Many organizations offer Farm-as-a-Service (FaaS), allowing you to access advanced machinery through leasing or subscription. This can lower the barrier to entry for smaller farms [2] .
- Plan for Infrastructure and Training: Implementing autonomous vehicles may require upgrading connectivity (such as installing Wi-Fi or 5G on your property) and investing in staff training. Many equipment providers and local agricultural cooperatives offer training programs-search for “autonomous farming training” and your region to find relevant resources.
- Leverage Data and Analytics: Integrate your autonomous vehicles with farm management software to monitor performance, optimize scheduling, and streamline decision-making. Consider consulting with precision agriculture experts for tailored advice.
For further guidance, consider contacting local agricultural extension services or university research programs specializing in precision agriculture and automation. They often provide consultations, field demonstrations, and access to pilot programs.
Challenges and Solutions: Bridging the Innovation Gap
Despite rapid innovation, practical adoption of autonomous agricultural vehicles comes with challenges:
1. Upfront Investment and Cost Barriers While prices for advanced equipment are dropping, initial investment can still be significant. Leasing, government incentives, and cooperatives may help offset costs. To explore available grants or incentives, visit the official website of your country’s department or ministry of agriculture and search for “agricultural innovation grants” or “precision farming funding.” Always verify program details through recognized government portals.
2. Technology Integration and Compatibility Integrating new autonomous systems with existing equipment and software often requires technical support. Manufacturers and agtech consultants can assist with integration and troubleshooting-reach out to your provider’s customer service or technical support channels for step-by-step guidance.

Photo by Igor Shalyminov on Unsplash
3. Data Privacy and Security As more farm data moves online, protecting sensitive information is critical. Use secure, reputable farm management platforms and regularly update your systems. Consult with IT specialists who focus on agricultural cybersecurity to develop best practices for your operation.
4. Skills Gap and Workforce Transition Transitioning to autonomous systems means upskilling workers and adapting management practices. Engage with local training initiatives or seek out online courses from established agricultural colleges and technical institutes.
Looking Ahead: Trends Shaping the Next Decade
The future of autonomous agricultural vehicles is dynamic and rapidly evolving. Key trends to watch include:
- AI-Driven Customization: Machines will increasingly adapt to specific crops, field conditions, and farm sizes, delivering tailored solutions for diverse agricultural needs [2] .
- Electrification and Alternative Energy: Expect a shift toward electric and hybrid vehicles, reducing energy costs and emissions.
- Integration with Drones and Aerial Robotics: Drones will play a larger role in crop monitoring, precision spraying, and even seed planting, especially in remote or challenging environments [1] .
- Farm-as-a-Service (FaaS) Expansion: Subscription and pay-per-use models will make advanced technology more accessible to medium and small-scale farms.
With these advancements, the future of farming will be more data-driven, efficient, and sustainable than ever before.
How to Stay Informed and Take the Next Step
To keep up with the latest developments, you can subscribe to industry newsletters, attend agricultural technology conferences, and participate in online forums dedicated to precision farming. For hands-on demonstrations and the opportunity to connect with technology providers, search for regional agtech expos or field days organized by universities and agricultural extension services.
For direct assistance, reach out to established manufacturers through their official websites or contact your local agricultural technology cooperative. If you are interested in pilot programs or research partnerships, universities and agricultural research institutes are excellent starting points.
References
- [1] Farmonaut (2025). Autonomous Agricultural Machinery Market: 2025 Trends.
- [2] Farmonaut (2025). Agricultural Machinery Industry Trends 2025: Top Innovations.
- [3] AgriNextCon (2025). How Autonomous Machines Are Revolutionizing Farming in 2025.
- [4] Intellias (2025). Autonomous Farming: Revolutionizing Agriculture with AI and Robotics.
MORE FROM couponnic.com